Most of the time cutting force acting on a tool is measured experimentally. But it is also important to predict quantity of cutting force and how different cutting parameters are affecting cutting force even before setting up the machining operation due to following reasons.
In order to design of mechanical structure of cutting machine which will withstand cutting force and thrust force effectively.To determine power consumption during machining process. This will help in selecting suitable motor drive.To predict tool life.To increase productivity
Cutting Terminology
The following figure describes important terminologies used in cutting force analysis.
 Fig.1 A tool under orthogonal cutting operationThe figure shows a case where tool velocity (V) and cutting edge are perpendicular to each other,this is known as orthogonal cutting. Here we are analyzing cutting force for an orthogonal cutting operation. Cutting force (Fc) is the force parallel to cutting tool velocity. Rake angle of cutting tool is represented by 'alpha'
Fig.1 A tool under orthogonal cutting operationThe figure shows a case where tool velocity (V) and cutting edge are perpendicular to each other,this is known as orthogonal cutting. Here we are analyzing cutting force for an orthogonal cutting operation. Cutting force (Fc) is the force parallel to cutting tool velocity. Rake angle of cutting tool is represented by 'alpha'
Forces Acting on the chip
If you make a free body analysis of the chip, forces acting on the chip would be as follows.
 Fig.2 Forces acting on the chip on tool side and shear plane sideAt cutting tool side due to motion of chip against tool there will be a frictional force and a normal force to support that. At material side thickness of the metal increases while it flows from uncut to cut portion. This thickness increase is due to inter planar slip between different metal layers. There should be a shear force (Fs) to support this phenomenon. According to shear plane theory this metal layer slip happens at single plane called shear plane. So shear force acts on shear plane. Angle of shear plane can approximately determined using shear plane theory analysis.It is as follows
Fig.2 Forces acting on the chip on tool side and shear plane sideAt cutting tool side due to motion of chip against tool there will be a frictional force and a normal force to support that. At material side thickness of the metal increases while it flows from uncut to cut portion. This thickness increase is due to inter planar slip between different metal layers. There should be a shear force (Fs) to support this phenomenon. According to shear plane theory this metal layer slip happens at single plane called shear plane. So shear force acts on shear plane. Angle of shear plane can approximately determined using shear plane theory analysis.It is as follows
Shear force on shear plane can be determined using shear strain rate and properties of material. A normal force (Fn) is also present perpendicular to shear plane. The resultant force (R) at cutting tool side and metal side should balance each other in order to make the chip in equilibrium. Direction of resultant force, R is determined as shown in Figure 2.
Merchant's Circle Analysis
Steps involved in Merchant's circle analysis is as follows. Since we know angle of resultant force at tool side, draw a line parallel to this. On one end of this line draw shear force(Fs), magnitude and direction of which is known. Now draw a line perpendicular to shear force line, it will meet resultant force line at one point. You can draw a circle assuming the intersected line as diameter of the circle, this is known as Merchant's circle. It is shown in figure below.
 Fig.3 Construction of Merchant's circleIn order to determine cutting force (Fc) one can draw a line parallel to tool motion in Merchant's circle, starting from end of diameter. The chord so obtained will give magnitude of cutting force. If you draw a line perpendicular to Fc that will give thrust force acting on the tool (Ft). So resultant force, R at tool side also can be considered as a summation of cutting force and and thrust force. The diagram so obtained is shown in following figure.
Fig.3 Construction of Merchant's circleIn order to determine cutting force (Fc) one can draw a line parallel to tool motion in Merchant's circle, starting from end of diameter. The chord so obtained will give magnitude of cutting force. If you draw a line perpendicular to Fc that will give thrust force acting on the tool (Ft). So resultant force, R at tool side also can be considered as a summation of cutting force and and thrust force. The diagram so obtained is shown in following figure. Fig.4 Determination of cuttin
Fig.4 Determination of cuttin
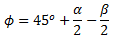
0 comments: